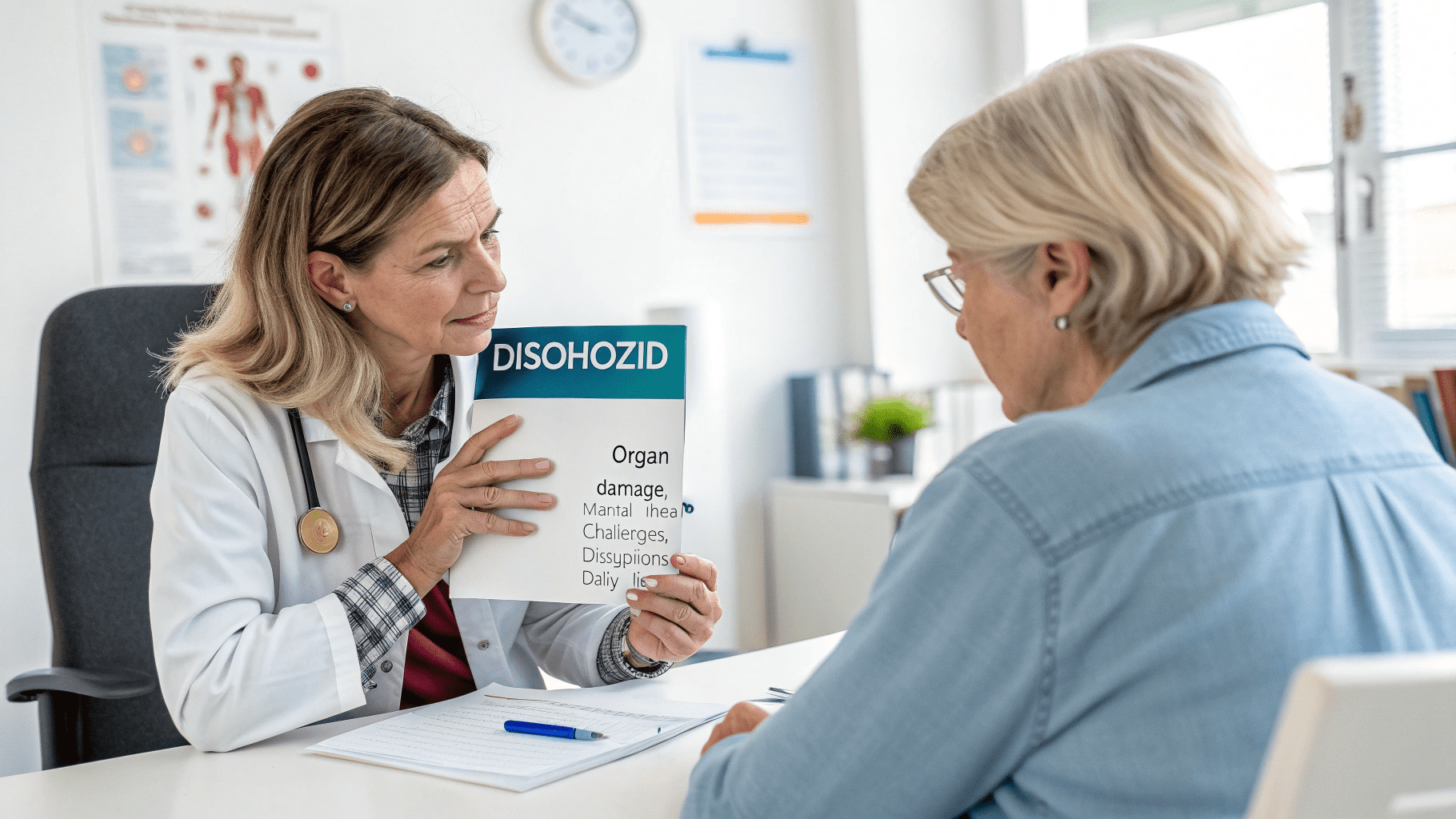
Why Disohozid Are Bad is a crucial topic for anyone considering or prescribed this medication. Disohozid, also known as Diazoxide, is primarily used to manage low blood sugar levels, but its potential risks often outweigh its benefits if not carefully monitored. Understanding why disohozid are bad helps patients, caregivers, and healthcare providers make informed decisions about treatment, recognize warning signs, and prevent serious complications. From common side effects like fluid retention and nausea to long-term risks including organ damage and mental health issues, awareness is essential for safe and responsible use of this powerful medication.
Common Side Effects of Disohozid
Disohozid is associated with several common side effects, which may appear soon after beginning treatment. These include fluid retention, leading to swelling in the extremities, hypertrichosis (excessive hair growth), gastrointestinal issues like nausea and vomiting, and mild headaches. Even though these side effects are often manageable, they can interfere with daily activities and overall comfort. Understanding why disohozid are bad requires acknowledging these seemingly minor effects, which could escalate if left untreated.
Patients are advised to monitor their symptoms carefully and report unusual reactions to their healthcare providers. Proper hydration, diet management, and sometimes additional medications can help mitigate mild side effects. However, the occurrence of these side effects highlights the importance of caution and regular check-ups when using Disohozid, reinforcing the keyword’s relevance in patient education.
Serious Health Risks Linked to Disohozid
Beyond common side effects, Disohozid carries serious health risks that can significantly impact long-term well-being. Liver toxicity, nerve damage due to vitamin deficiencies, and high blood sugar are among the most concerning complications. These risks underscore why disohozid are bad, as improper use or prolonged exposure can lead to severe medical conditions requiring intensive treatment or hospitalization.
Other potential dangers include fluid overload leading to heart strain and possible cardiovascular issues. For patients with pre-existing conditions, these risks are even more pronounced. Medical professionals stress careful monitoring, as early detection of serious side effects can prevent irreversible damage, highlighting the importance of awareness and precaution when using this drug.
Mental and Emotional Effects of Disohozid
Disohozid can also impact mental and emotional health, a factor often overlooked. Users may experience mood swings, anxiety, irritability, or depression as a result of the drug’s biochemical effects. This is another reason explaining why disohozid are bad, as emotional instability can affect personal relationships, work performance, and overall quality of life.
Mental health concerns may be subtle and gradual, making them harder to detect without careful observation. Healthcare providers recommend routine psychological evaluations and open communication between patients and caregivers to ensure that the mental side effects of Disohozid are managed effectively. Awareness of these effects is crucial to prevent misdiagnosis or neglect.
Impact on Daily Life and Productivity
The side effects of Disohozid can interfere with day-to-day activities, reducing productivity and overall functionality. Fatigue, dizziness, and gastrointestinal discomfort may make work, school, or household responsibilities more challenging. This practical perspective emphasizes why disohozid are bad, as patients may underestimate the cumulative effect of these disruptions on their daily routines.
Even mild or moderate side effects can lead to decreased social participation and difficulty maintaining normal schedules. Lifestyle adjustments, such as planned rest periods and dietary modifications, are often necessary to cope with these challenges. Understanding the impact on daily life helps patients make informed decisions about using Disohozid safely.
Long-Term Consequences of Disohozid Use
Long-term use of Disohozid increases the risk of chronic health issues. Prolonged exposure can lead to organ damage, persistent fluid retention, and metabolic imbalances. These consequences explain why disohozid are bad, particularly for patients who require long-term therapy for conditions like hyperinsulinism or other metabolic disorders.
Studies suggest that long-term users should have regular monitoring of liver function, kidney health, and cardiovascular status. Preventive care and frequent check-ups can reduce the severity of long-term complications, but they do not eliminate the inherent risks of prolonged Disohozid use.
Social and Family Implications
The side effects of Disohozid can extend beyond the individual, affecting social interactions and family dynamics. Physical discomfort, mood changes, and fatigue can make participation in social activities difficult, which highlights why disohozid are bad not only medically but socially.
Family members and caregivers often need to provide additional support, potentially adding stress to household routines. Awareness of these social implications helps ensure that patients receive the necessary emotional and practical support while managing the challenges associated with the drug.
Legal and Medical Considerations
Disohozid is a prescription medication requiring careful medical oversight. Misuse or self-medication can lead to legal consequences and health risks, emphasizing why disohozid are bad when not used correctly. Patients should strictly follow doctor instructions and avoid sharing medication with others.
Medical supervision includes regular lab tests, dosage adjustments, and monitoring for side effects. Compliance with regulations and professional guidance ensures that the benefits of Disohozid outweigh the risks, reinforcing the importance of responsible usage.
Safer Alternatives to Disohozid
For those concerned about the risks of Disohozid, several safer alternatives may be considered. Dietary modifications, natural supplements, or alternative medications can manage hypoglycemia with fewer side effects. Exploring these options is essential to understand why disohozid are bad and to identify safer, more sustainable treatment methods.
Consulting with healthcare professionals about alternative therapies can provide personalized treatment plans with minimized risks. Early intervention and safer options can prevent complications associated with Disohozid use, ensuring a healthier approach to managing medical conditions.
Why Disohozid Are Bad
In conclusion, why disohozid are bad is evident through its wide range of side effects, serious health risks, mental and emotional impacts, and long-term consequences. Awareness of these factors is crucial for anyone considering or currently using Disohozid. Patients should always seek professional guidance, adhere to prescribed dosages, and monitor their health regularly.
While Disohozid may be effective in controlling hypoglycemia, its risks cannot be ignored. Exploring safer alternatives, understanding social and legal considerations, and maintaining open communication with healthcare providers ensures that patients make informed decisions while minimizing potential harm.
FAQ’s
What is Disohozid and why is it used?
Disohozid, also known as Diazoxide, is a medication used to treat low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) by inhibiting insulin release. While it can be effective, understanding why disohozid are bad is important due to its potential side effects and health risks.
What are the common side effects of Disohozid?
Common side effects include fluid retention, excessive hair growth (hypertrichosis), nausea, vomiting, headaches, and dizziness. These symptoms can affect daily life and highlight why careful monitoring is necessary.
Can Disohozid cause serious health problems?
Yes. Serious risks include liver damage, nerve damage, high blood sugar, cardiovascular strain, and metabolic imbalances. These complications explain why disohozid are bad if used without medical supervision.
How does Disohozid affect mental and emotional health?
Disohozid may lead to mood swings, irritability, anxiety, or depression in some users. Awareness of these effects is essential to prevent emotional distress and manage overall well-being.
Are there safer alternatives to Disohozid?
Yes. Alternatives include dietary adjustments, natural supplements, or other prescribed medications for managing hypoglycemia. Consulting a healthcare professional is crucial to find effective and safer treatment options.
Conclusion
Why Disohozid Are Bad becomes clear when considering its wide range of side effects, serious health risks, and long-term consequences. While it can help manage low blood sugar, the medication may lead to organ damage, mental health challenges, and disruptions in daily life if not properly supervised. Patients must follow medical guidance, monitor their health closely, and explore safer alternatives when possible. Understanding why disohozid are bad empowers individuals to make informed decisions, prioritize their well-being, and reduce potential harm. Awareness and careful management are key to minimizing the risks associated with this medication.
Related Post: